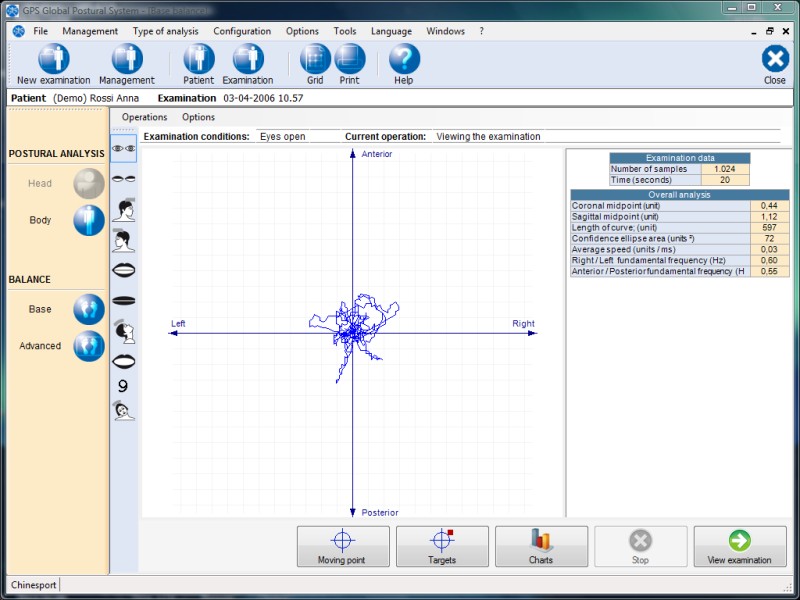
Numeric values are calculated after a test and can be divided into two groups:
Example:

Number of samples
It is the number of samples performed during the test over a period of time.
Time (seconds)
It is the test duration expressed in seconds.
Coronal midpoint (unit)
It is the distance in units between the average of the measurements projected on the right / left axis and the origin of the Cartesian axes.
In other words, it is a value indicating the distance between the patient's average center of gravity on the right / left axis and the ideal center.
Sagittal midpoint (unit)
It is the distance in units between the average of the measurements projected on the anterior / posterior axis and the origin of the Cartesian axes.
In other words, it is a value indicating the distance between the patient's average center of gravity on the anterior / posterior axis and the ideal center.
Length of curve (unit)
It is the length in units of the patient's center of gravity shift during the test.
Confidence ellipse area at 90% (units˛)
It is the area in units˛ of the ellipse that includes all the center of gravity points measured and transferred on a system of Cartesian axes with a confidence level of 90%.
A 90% confidence refers to a statistical calculation meant to exclude extreme shifts of the center of gravity from the area calculation.
Average speed (units / ms)
It is the average speed of the average center of gravity shift in units /millisecond.
Right / Left fundamental frequency (Hz)
It is the fundamental frequency of oscillation in the right / left direction, expressed in Hertz.
Anterior / Posterior fundamental frequency (Hz)
It is the fundamental frequency of oscillation in the anterior / posterior direction, expressed in Hertz.
Manual GPS 5, version 1.0.5 release date:14-01-2011 Copyright © 2011 Chinesport